What's It Like to Be a Sound Engineer?

Imagine you're a sound engineer, balancing technical expertise with creative intuition. Your day begins with pre-session preparation, ensuring all equipment is set up and functioning correctly. As the recording process starts, you're not just pressing buttons; you're capturing the essence of the performance. Editing and mixing follow, where you transform raw audio into a polished product. However, the role involves more than just these tasks—technical troubleshooting and post-production responsibilities add layers of complexity. Curious about the blend of creativity and precision that defines this career? Let's explore the intricacies further.
Pre-Session Preparation

Effective pre-session preparation starts with clear communication with your clients to understand their specific requirements and expectations for the recording session. This step ensures alignment with their vision and allows you to tailor the technical setup accordingly.
Next, focus on setting up your audio equipment. Verify that microphones, mixers, and other essential gear are correctly positioned and functioning. This preparation helps capture optimal sound quality from the outset. Additionally, check the functionality of your recording devices, such as Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) or tape machines, to identify and resolve any technical issues before the session begins, thus avoiding unexpected interruptions.
Equally important is configuring your recording environment. Proper acoustic treatments and sound isolation are crucial for achieving high-quality sound. Adjust these elements based on the specific needs of your session to minimize unwanted noise and reflections.
Recording Process
The recording process requires a high level of collaboration between you, the musicians, and the producers to capture sound accurately. Real-time monitoring and adjustments to recording levels are necessary as the session progresses. Flexibility is essential for audio engineers, as you must adapt your setup based on artist feedback and the evolving sound quality.
Clear communication with your team is crucial. Throughout the session, ensuring everyone is aligned is key to achieving the desired sonic results. You will select and use various microphones and mixers, matching the appropriate equipment to each instrument and vocal technique. This necessitates a deep understanding of how different gear influences sound.
The recording environment also plays a critical role. You must configure the space effectively, often incorporating acoustic treatments to minimize unwanted sound reflections and background noise. This step is fundamental for capturing high-quality audio. By fine-tuning both the setup and the room, you ensure every aspect of the recording is captured effectively, making the entire process smoother and more efficient. This meticulous attention to detail distinguishes a great audio engineer.
Editing and Mixing

When you move on to editing and mixing, you delve into the core of crafting the final sound. During editing, you'll meticulously review multiple takes, selecting the best parts to create cohesive tracks. This stage is crucial for enhancing the listener's overall experience. It's important to document every change and maintain well-organized session files to ensure an efficient workflow and facilitate future audio production needs.
Mixing, in contrast, involves applying techniques such as EQ and compression to balance and harmonize the song's elements. Your refined listening skills will help you avoid cluttered sounds and highlight key track elements for clarity. Collaboration with artists and producers is often essential in mixing, ensuring the final sound aligns with their creative vision and expectations.
Sound engineers must master these technical aspects to transform raw recordings into polished tracks. This process demands not only technical expertise but also a keen ear and a collaborative spirit. By excelling in editing and mixing, you significantly contribute to the art of audio production, making each song resonate with its intended audience.
Post-Production Tasks
Post-production tasks for sound engineers are crucial for enhancing audio clarity and quality. This phase involves meticulously editing audio tracks to remove unwanted noise and refine each element, ensuring crystal-clear sound. Synchronizing audio with video is another key task, essential for creating a seamless multimedia experience.
During post-production, you'll apply improvements and effects based on client specifications, utilizing various plug-ins and software tools to achieve the desired auditory outcome. Collaboration is vital in this stage; you'll work closely with sound designers and composers to finalize the sound design.
Meeting industry standards and client expectations is paramount. A thorough review process is necessary to ensure the final audio product is flawless before release. By meticulously editing audio and collaborating with your team, you contribute to producing a polished, professional sound. Embrace the challenges of post-production to deliver high-quality audio that meets rigorous scrutiny.
Technical Troubleshooting
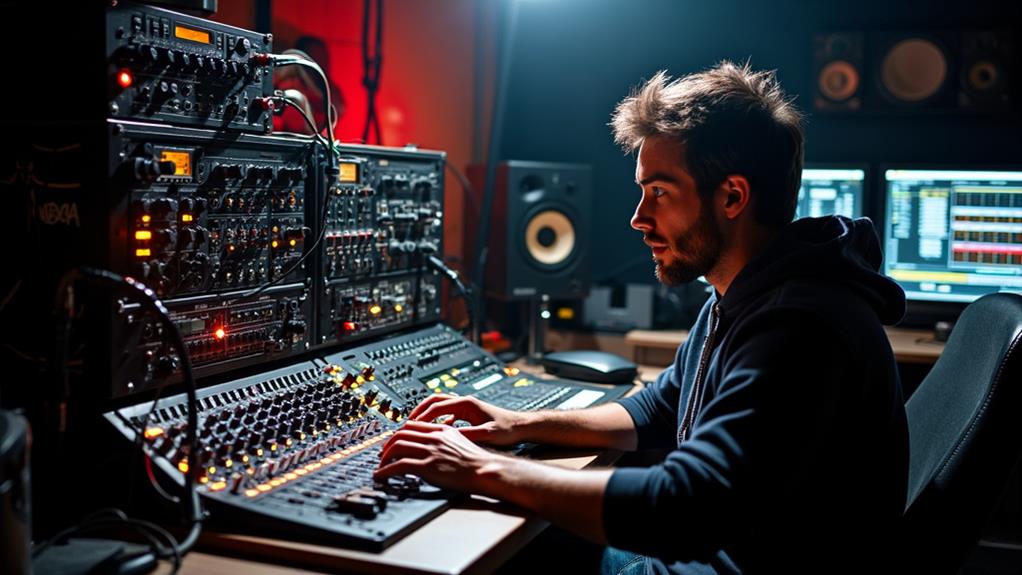

Sound engineers frequently face situations where technical troubleshooting is essential for maintaining a seamless recording session. When issues arise, your diagnostic skills become crucial. You must quickly identify problems such as microphone malfunctions, cable failures, or software glitches to ensure minimal disruption to the workflow.
Being proficient in troubleshooting both hardware and software components is vital. Regular maintenance, including cleaning connectors and testing devices, can prevent many technical problems. However, when issues do occur, your understanding of acoustics and signal flow helps you identify problems that affect sound quality, like feedback loops or phase cancellation. Swiftly resolving these issues is vital for producing high-quality audio.
Staying current with the latest technology and industry trends is another critical aspect of effective troubleshooting. New equipment and software features may introduce unique challenges but also offer new solutions. By keeping your skills sharp and your tools well-maintained, you're better prepared to handle any technical issues, ensuring that your recording sessions run smoothly and efficiently.
Creative Aspects
Exploring the creative aspects of being a sound engineer reveals that it encompasses both technical expertise and artistic expression. Sound engineers are vital in transforming basic sounds into intricate tracks by creatively layering and manipulating various audio elements to achieve the desired sonic textures. This involves the art of sound design, where innovative techniques and effects are used to evoke emotions and enhance storytelling, particularly in multimedia projects.
During the editing process, sound engineers utilize their keen listening skills to select the best takes and eliminate imperfections, thereby enhancing the overall auditory experience. In the mixing phase, balancing different components of a track is crucial. Precise listening skills ensure clarity and cohesion, highlighting essential elements like vocals or lead instruments.
Another significant aspect is creative collaboration with artists. Sound engineers blend their technical expertise with the unique styles and preferences of musicians, significantly contributing to the artistic vision of each project. This dynamic interaction not only brings out the best in a track but also fosters professional growth, allowing sound engineers to continuously refine their craft and push the boundaries of audio engineering.
Industry Dynamics
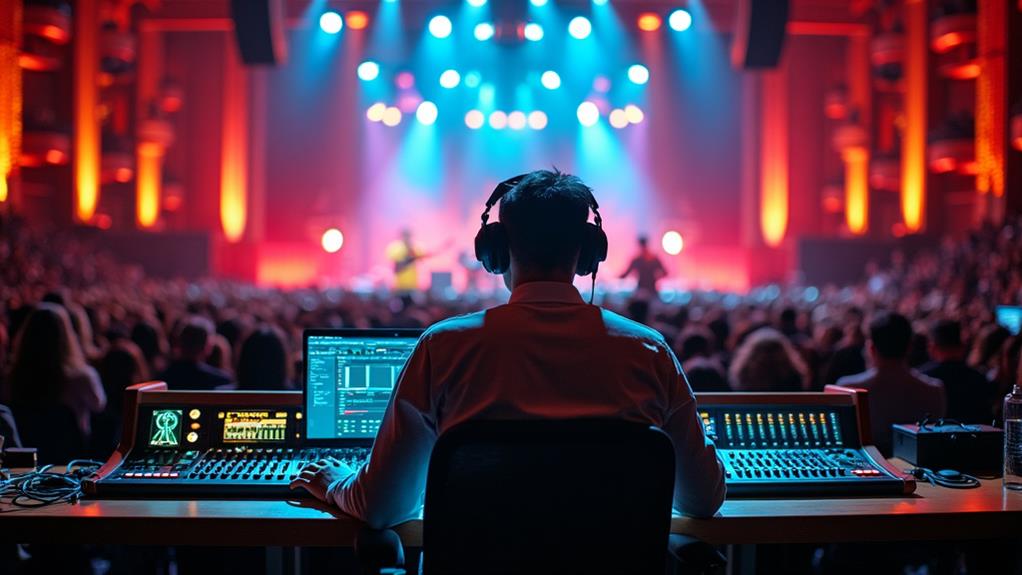

As a sound engineer, you will encounter diverse career opportunities in music, film, television, live sound, and broadcasting. Each environment presents unique challenges that require you to adapt your skills to different audio setups. Flexibility and strong networking are crucial for success in this dynamic industry.
Diverse Career Opportunities
Audio engineering presents a diverse array of career opportunities across multiple industries, underscoring the versatility and significance of this skill set. In this dynamic field, professionals can find roles in the music industry, film, television, live sound, and broadcasting. The role of an audio engineer is multifaceted, blending technical proficiency with creative ingenuity. The job outlook for audio engineers is promising, with a projected growth rate of 21% from 2020 to 2030, significantly surpassing the average for all occupations.
As an audio engineer, you have the option to specialize in various roles such as recording engineer, mixing engineer, mastering engineer, and live sound technician. Each specialization demands a unique set of skills and expertise, allowing you to tailor your career to your specific strengths and interests. Freelancing is prevalent in this field, offering opportunities to work on a wide range of projects, from studio recordings to live events, thereby helping you build a diverse portfolio and extensive network.
Furthermore, the demand for audio engineering skills extends beyond traditional settings. Industries like advertising and computer system design also seek these skills, often offering higher wages. This broad applicability makes audio engineering a dynamic and rewarding career choice.
Adapting to Environments
Navigating the dynamic landscape of audio engineering requires a keen ability to adapt to varied environments. As a sound engineer, you might find yourself working in studios, live venues, theaters, or on film sets. Each environment demands different technical setups and approaches. Your responsibility is to ensure high-quality audio, which requires a flexible skill set to address the unique challenges of music production, broadcasting, film scoring, and live sound events.
Adapting to different acoustics and sound behaviors necessitates a deep understanding of acoustics and sound design principles. Quick troubleshooting of technical issues is essential for maintaining smooth operations. Many sound engineers work on a freelance basis, allowing them to navigate a range of audio-focused industries and projects, enhancing adaptability and expanding networking opportunities.
The job market for sound engineers is projected to grow by 21% from 2020 to 2030, reflecting the increasing demand for skilled professionals. To succeed, consider these key points:
- Develop a versatile skill set for different audio environments.
- Master acoustics and sound design principles to adapt quickly.
- Improve troubleshooting skills to handle technical issues efficiently.