What's It Like to Be a Professional Sculptor?
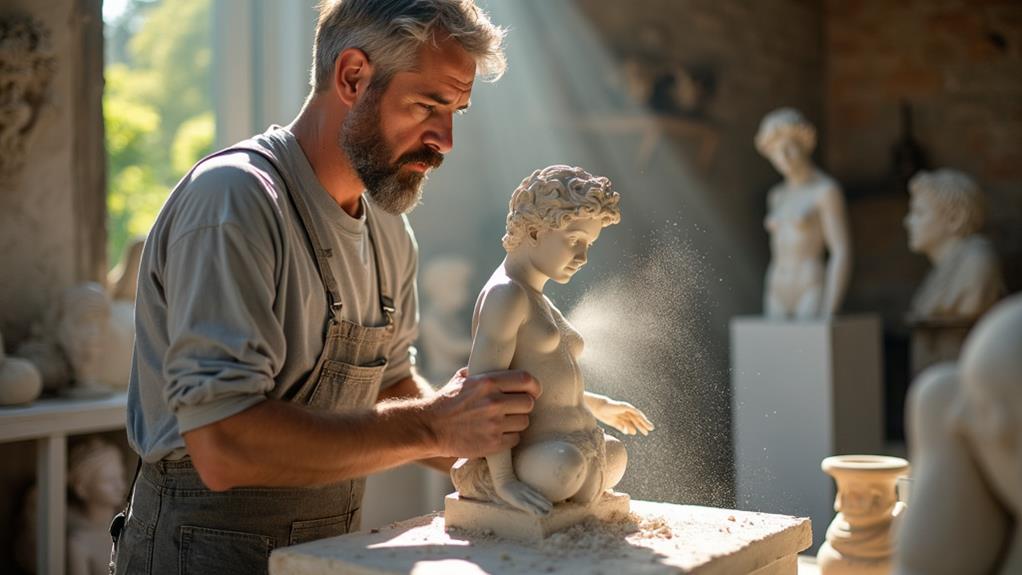

Imagine shaping raw materials into evocative forms, balancing creativity and technical skill daily. As a professional sculptor, you navigate the unpredictable nature of your medium and the physical demands of your craft. Your journey involves building a diverse portfolio, innovating to stand out, and aligning your work with community aesthetics for public commissions. Continuous professional development and advocacy for the arts are crucial. But what specific challenges do sculptors face, and how do they tell unique stories through their creations? Let's delve into it.
Role of a Sculptor
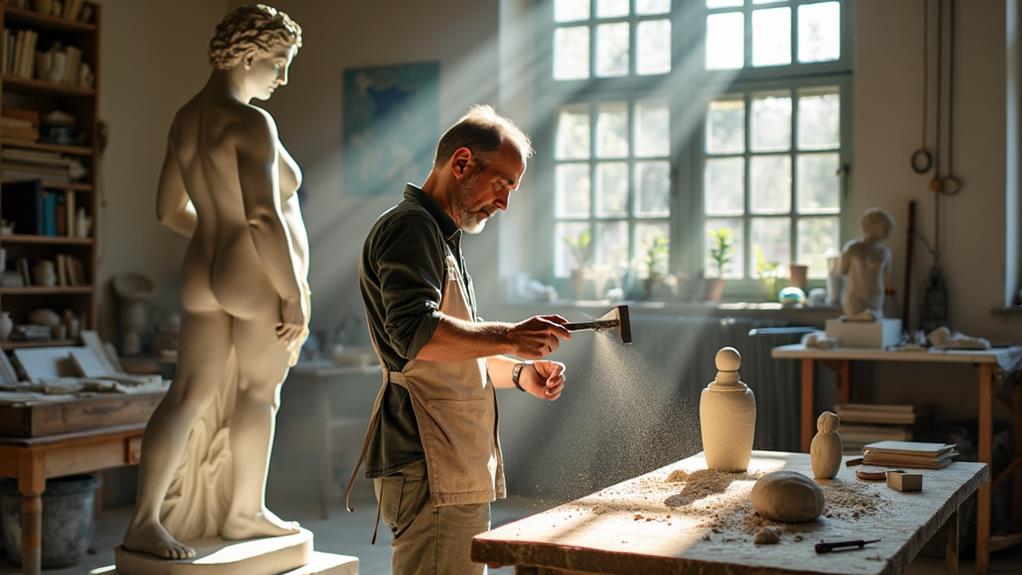

As a sculptor, you transform raw materials like stone, wood, metal, and plastic into captivating two- or three-dimensional artworks. This role requires a deep understanding of these materials and the techniques needed to manipulate them effectively. Whether carving marble, casting bronze, or using 3D printing for modern creations, each material poses unique challenges and opportunities.
Traditional methods such as carving and relief are often employed to bring your visions to life, while contemporary techniques and modern technology ensure your work remains innovative. Public commissions, in particular, demand flexibility and creativity, as you must tailor your creations to meet the cultural and aesthetic expectations of the communities or institutions where your sculptures will be displayed.
Selling your work through galleries and exhibitions is another crucial aspect of your role. These venues provide a platform to showcase your portfolio, which is vital for attracting both private and public commissions. Your portfolio is more than just a collection of your best pieces; it serves as your artistic resume, demonstrating your range and skill to potential clients and institutions.
Educational Pathways
To become a professional sculptor, formal qualifications are not mandatory. However, pursuing a degree such as a BA in Fine Art Sculpture can significantly enhance your skills. Admission to these programs typically requires a strong portfolio and foundational courses like a Foundation Studies diploma or A levels. Advanced training through postgraduate degrees and specialized courses can further refine your artistic abilities.
Degrees and Qualifications
While formal qualifications aren't strictly necessary to become a sculptor, obtaining a BA (Hons) in Fine Art Sculpture can significantly enhance your skills and artistic vision. Degrees and certifications in this field offer structured learning and exposure to various techniques and materials. Admission to most colleges and universities typically requires a strong portfolio and foundational art education, such as a foundation studies diploma in art and design or 2-3 A levels.
For those beginning their journey, Level 2 and Level 3 Art and Design courses are invaluable for building fundamental and advanced sculpting skills. These courses cover essential techniques and foster a deep understanding of different artistic mediums. For further skill refinement, postgraduate degrees and specialized courses offer advanced training, elevating both technical abilities and artistic perspectives.
Practical experience is equally important. Workshops, mentorships, and internships in sculptor studios provide hands-on learning that complements academic knowledge. These opportunities enable you to apply theoretical concepts in real-world settings, fostering growth as both an artist and a professional. While degrees and qualifications are not mandatory, they do provide a strong foundation for a successful sculpting career.
Building a Portfolio
Building a strong portfolio is your next critical step after acquiring foundational skills and qualifications. Your portfolio serves as your artistic resume, showcasing a variety of skills and styles that demonstrate your potential. Many art institutions, such as Camberwell College of Arts, require a robust portfolio for entry into programs like their BA (Hons) Fine Art Sculpture.
To build a compelling portfolio, consider completing a foundation studies diploma in art and design. This can help you refine your skills and provide a broader range of work to include. Additionally, achieving 2-3 A levels can enhance your educational background, making your portfolio even more impressive to admissions committees.
Practical experience is also invaluable. Engage in internships or workshops in sculpture studios to gain hands-on experience and diversify your portfolio. These opportunities allow you to experiment with different materials and techniques, adding depth and variety to your work.
Advanced Training Options
Many aspiring sculptors find that pursuing advanced training options significantly enhances their artistic and technical skills. While formal qualifications are not mandatory, enrolling in a BA (Hons) Fine Art Sculpture program, such as the one at Camberwell College of Arts, can greatly improve your artistic practice and skill set. Admission to such programs typically requires a foundation studies diploma in art and design or 2-3 A levels, along with a strong portfolio showcasing your work.
Beyond undergraduate degrees, advanced training options include postgraduate degrees and specialist courses. These programs offer in-depth study and technical skill improvement, providing a deeper understanding of diverse sculpting techniques and materials. Level 2 and Level 3 Art and Design courses are also available, offering foundational and advanced training to build your sculpting skills from the ground up.
In addition to formal education, practical experience is essential for developing as a sculptor. Working in sculptor studios, participating in workshops, and engaging in mentorship programs can significantly contribute to your skill acquisition and artistic growth. These hands-on experiences allow you to refine your techniques and gain valuable insights from established professionals in the field.
College Courses

Aspiring sculptors frequently discover that college courses provide a critical foundation for their artistic journey. Typically, the first step is Level 2 Art and Design courses, which focus on foundational skills. As students advance, Level 3 courses delve into more sophisticated techniques and materials. Many institutions also offer specialized programs, such as a BA (Hons) in Fine Art Sculpture, aimed at refining your craft further.
Here is an overview of what different college courses might offer:
| Course Level | Focus Areas |
|---|---|
| Level 2 Art and Design | Foundational skills |
| Level 3 Art and Design | Advanced techniques and materials |
| BA (Hons) Fine Art Sculpture | Specialized sculpture training |
| Short Courses | Skill development without long-term commitment |
| Workshops | Hands-on practical experience |
Short courses and workshops allow you to explore sculpture without the commitment of a long-term program. These options are ideal for gaining practical experience and building a strong portfolio, which is often required for admission to advanced programs.
Resources and Organizations
As a professional sculptor, you can access invaluable support and resources through various organizations and networks. The National Society for Education in Art and Design provides educational tools to foster your development, while the Guild Society of Artists offers networking and mentorship opportunities. Additionally, the Sculptors Guild and Artquest focus on advocacy, community building, and essential career guidance. Arts Council England also plays a critical role by offering significant funding and increasing visibility for artists.
Educational Support Networks
Navigating the journey to becoming a professional sculptor can be both challenging and rewarding, especially with the right support networks and resources. Educational support networks are instrumental in honing your skills and expanding your knowledge. Organizations like the National Society for Education in Art and Design offer extensive resources and support for art educators and students, focusing on enriching your sculpture education with the latest techniques and teaching methods.
Networking opportunities are equally vital. The Guild Society of Artists provides a platform for connecting with fellow sculptors, fostering collaboration, and promoting professional growth. Through these networks, you can share ideas, gain insights from peers, and find mentors to guide your artistic journey.
Advocacy and community engagement are also crucial. The Sculptors Guild advocates for sculptors, offering resources and a community platform to promote sculpture as an art form. Financial support is another key aspect of sustaining your practice. Artquest provides valuable information and funding opportunities tailored for artists, helping you navigate the often complex financial landscape.
Additionally, organizations like Arts Council England support your projects and career development through various arts initiatives, ensuring you have the resources needed to succeed.
Professional Development Opportunities
Professional development opportunities are crucial for elevating your sculpting career. These resources and organizations play a key role in enhancing your skills, expanding your network, and promoting your work within the art and design community.
- National Society for Education in Art and Design: This organization offers educational resources and support to help you refine your teaching and artistic practices. Engaging with their programs can significantly boost your professional profile.
- Guild Society of Artists: By providing networking opportunities and advocacy, this society fosters collaboration and community among sculptors. Participating in their events and initiatives can greatly expand your professional connections.
- Artquest: This platform provides valuable information and funding opportunities specifically tailored for artists. If you're seeking grants or project support, Artquest is an essential resource for sustaining and growing your career.
- Arts Council England: This council plays a key role in supporting arts initiatives by offering funding and resources to sculptors. Their backing can be instrumental in bringing your artistic visions to life and contributing to the broader artistic community.
Utilizing these professional development opportunities will not only enhance your skills but also ensure your long-term success in the dynamic world of art and design.
Advocacy and Community Building
Connecting with the right resources and organizations can be transformative for your sculpting career, fostering both advocacy and community building. The National Society for Education in Art and Design offers invaluable educational resources and advocacy, emphasizing the importance of art in schools and communities. By aligning with such organizations, you can help promote and sustain the value of art in society.
The Guild Society of Artists provides excellent networking opportunities, support, and resources specifically for sculptors. Engaging with this guild allows you to connect with peers, share experiences, and enhance your professional development. Whether seeking advice on technique or exploring new materials, this network can be an essential support system.
Community building is a core focus of the Sculptors Guild, creating a platform for sculptors to share their work, ideas, and challenges. It's an ideal space for fostering collaborations and advocating for the unique needs of sculptors within the broader art community.
Artquest is another key resource, offering critical information and funding opportunities to help navigate the often complex landscape of financial support. Similarly, Arts Council England provides essential funding and resources, enabling sculptors to thrive in their creative endeavors. Joining these organizations can significantly bolster your advocacy efforts and strengthen your community ties.
Featured Sculptor
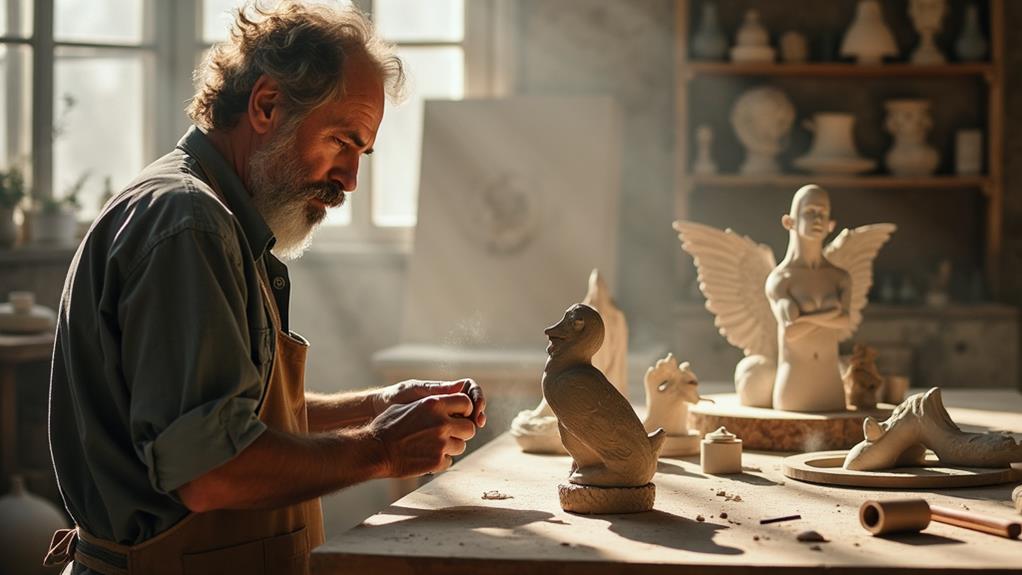

In contemporary sculpture, Dylan Shields is a standout artist who skillfully merges traditional narrative painting techniques with modern materials. His sculptures, crafted from recycled cardboard and parcel tape, breathe life into forgotten narratives. Shields' work transcends mere form, delving into deeper themes that blend art history with modern societal contexts, urging viewers to rethink conventional perceptions of sculpture.
Key aspects of Shields' work include:
- Innovative Materials: He employs recycled cardboard and parcel tape, breaking away from traditional sculpting mediums.
- Narrative Richness: His sculptures narrate forgotten stories, intertwining historical and contemporary themes.
- Sustainability: By using recycled materials, Shields highlights the importance of sustainability in art.
- Acclaim: His innovative techniques have garnered significant recognition in the art world, underscoring his role in redefining sculpture.
Shields' transformative use of everyday materials into compelling forms showcases the potential for contemporary artists to innovate and inspire. By merging the familiar with the unexpected, he challenges viewers to see art through a new lens, proving that sculpture can be both sustainable and profoundly impactful.
Career Challenges
Shields' innovative approach to sculpture not only redefines the medium but also underscores the numerous challenges sculptors face. A significant career challenge is the physical toll of sculpting, with repetitive strain injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, being common due to the extensive manual labor involved. Your hands, wrists, and back often bear the brunt of your creative efforts.
Materials present another set of obstacles. The unpredictability of materials, such as the varying consistency of cheese or the fragility of ice, can complicate your work and impact the final result. Time constraints, particularly during live events, add pressure, potentially compromising the structural integrity and overall quality of larger pieces.
Preservation is another critical issue, especially for perishable materials like cheese. Proper refrigeration and careful handling are essential to prevent deterioration, adding complexity to your career challenges.
Lastly, competition is intense. As more sculptors enter the field, the standards for quality continue to rise. To remain relevant and successful, you must constantly innovate and refine your skills. Balancing these challenges can be demanding but also incredibly rewarding, driving you to new heights in your artistic journey.